Asia has a history extending back to the ancient period. East Asian, West Asian, and South Asian civilizations did emerge independently of one another, but there is a common factor among them. The river valley systems are what sustained survival in these locations. The Tigris and Euphrates rivers in Mesopotamia provided numerous states and empires a base to build. The Indus Valley was the foundation of Indian civilization. China's base of civilization would be the Huang He River ( Yellow River). Empires emerged that included the Han Dynasty, Sumer, Akkad, Annam, Gupta, Champa, Khmer, and many more. The Pacific Ocean islands also saw the development of indigenous societies. Polynesians navigated the waters frequently before European arrival. At one point it seemed as if Asian civilization would have hegemony over the world. The Age of Exploration changed this has European states began to find new trade routes and establish overseas colonies. When the 19th century came, Asia found itself under European colonization. Ottoman Turkey and Japan were exceptions to the rule. The Ottoman Empire by 1878 was weakened to the point of being referred to as "the sick man of Europe." Japan when through a program of intense modernization and industrialization to avoid European conquest. It stated imperial expansion of its own, which would eventually lead it to conflict with European powers. After World War II, Asian nations fought for independence from their former colonizers. Asia became another battle ground in the Cold War and the wars in Indochina became a lasting symbol of that. The collapse of the Soviet Union caused more complications as the US sought to become a global enforcer, forming increasing tensions with China. The 21st century could see an Asian resurgence as China and India are becoming more important to international markets.
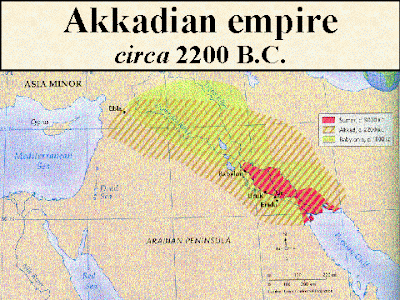
Southwest Asia has a long history dating back as far as 2800 B.C.E. Major states and kingdoms included Sumer, Akkad, and Babylonia. This entire region was known as Mesopotamia (now modern day Iraq). The Assyrian Empire emerged and fell around 612 B.C.E. The Euphrates and the Tigris river were the foundations of the civilization of the Levant. The area was under constant threat from invaders. Assyria fell due to a combination of Persian, Babylonian, and Medes invasion. The Babylonians who ruled under a Chaldean dynasty would be conquered by the Persians in 539 B.C.E. The Persians would dominate the Levant, until they faced a challenge from the Greeks. Cyrus the Great built the empire into a mighty force. Darius I was the king to consolidate the administrative structure of the Persian Empire. Alexander the Great a Macedonian warrior king, had united Greece and sought to build an empire of his own. Around 330 B.C.E Alexander targeted the Persian Empire for conquest. The Persian Empire was in disarray from the onslaught. Only when Alexander died from a fever did Persia recover gradually. Parthia became a successor empire and its competitor became the Roman Empire in the Middle East. A real threat came when Rome added Syria to its territories in 63 B.C.E. The Parthian Empire would collapse and the Sassanians then took control of Persia. They would also be in conflict with Rome's successor empire Byzantium.Besides being an area of empires, the Middle East gave birth to the world's most prominent religions. Islam, Christianity, and Judaism emerged from the Levant. These religions have an eclectic mix of ideas and philosophies that predate their existence. Zoroastrianism had articulated the monotheistic concept and many ideas from that Persian religion can be seen in Islam, Christianity, and Judaism.
Southwest Asia has a long history dating back as far as 2800 B.C.E. Major states and kingdoms included Sumer, Akkad, and Babylonia. This entire region was known as Mesopotamia (now modern day Iraq). The Assyrian Empire emerged and fell around 612 B.C.E. The Euphrates and the Tigris river were the foundations of the civilization of the Levant. The area was under constant threat from invaders. Assyria fell due to a combination of Persian, Babylonian, and Medes invasion. The Babylonians who ruled under a Chaldean dynasty would be conquered by the Persians in 539 B.C.E. The Persians would dominate the Levant, until they faced a challenge from the Greeks. Cyrus the Great built the empire into a mighty force. Darius I was the king to consolidate the administrative structure of the Persian Empire. Alexander the Great a Macedonian warrior king, had united Greece and sought to build an empire of his own. Around 330 B.C.E Alexander targeted the Persian Empire for conquest. The Persian Empire was in disarray from the onslaught. Only when Alexander died from a fever did Persia recover gradually. Parthia became a successor empire and its competitor became the Roman Empire in the Middle East. A real threat came when Rome added Syria to its territories in 63 B.C.E. The Parthian Empire would collapse and the Sassanians then took control of Persia. They would also be in conflict with Rome's successor empire Byzantium.Besides being an area of empires, the Middle East gave birth to the world's most prominent religions. Islam, Christianity, and Judaism emerged from the Levant. These religions have an eclectic mix of ideas and philosophies that predate their existence. Zoroastrianism had articulated the monotheistic concept and many ideas from that Persian religion can be seen in Islam, Christianity, and Judaism.
The ironic twist is that these monotheistic religions could be a source of contention or unity. The Islamic empires that emerged kept the region stable. The Umayyad and Abbasid caliphates allowed for a low level of conflict. That did not stop Turkish invaders form conquering it. After the two caliphates collapsed the Ottoman Empire would take its place. It would remain a dominant power up until the 19th century, when European power surpassed it.
India and China were two major forces through out Asian history. India's history can be traced back to the 4th millennium. India had commercial links with Southwest Asia. Often it is a mistake made to assume that ancient civilizations were isolated. Various peoples made contact, but the extent is still unknown. Many were probably aware that the world was much larger than their immediate region. Dravidians were the original inhabitants of India, who were later invaded by the Aryans. These Central Asian warriors entered the area between 1500 and 1200 B.C.E. The Aryans brought with them a Sanskrit writing system and Indo-European language. The Indus Valley was also being transformed with the introduction of new ideas. Hinduism emerged from a combination of Aryan religious convictions and Dravidian customs. Around the 6th century B.C.E other religions would appear. Jainism and Buddhism appeared in the Indus Valley region. Buddhism would spread to East and Southeast Asia, but would have limited influence in the place of its inception. Under Chandragupta Maurya the Magadha Kingdom was invaded, starting the process of building a vast subcontinent empire. Access to the Ganges Valley increased the power of any king who successfully procured it. Asoka reign expanded what his grandfather started. He would dominate the Indian Subcontinent from 274 to 232 B.C.E. Chandragupta I would eventually expanded his territory and accomplished the unification of the Indian subcontinent. He established himself through invasions north around 320 C.E. Afterwards India was under the rule of the Gupta dynasty. They would remain the most powerful political force for 200 years.
China has some similarities in its historical path. The foundation of Chinese civilization like India is the river valley system. China also like India was never a fully unified empire when it emerged. The earliest Chinese dynasty was Xia and rose from the Huang He Valley. This occurred around 2000 B.C.E. There was another dynasty that became a rival known as the Shang. Based in the north, it was more powerful reaching a level of prominence in 1400 B.C.E. The Shang would be deposed by the Zhou by 1027 B.C.E. Major disorder occurred during the Warring States Period. Confucius would emerge with political and ethical philosophy that still has influence on East Asia today. Respect for one's elders, conducting government in an ethical manner, and valuing knowledge were critical attributes of Confucian thought. The insurrection and disorder in China did not last long, when the state of Qin grew in power. The Han dynasty came to power in 206 B.C.E and they successfully subdued invaders from the north. The establishment of the Great Wall allowed for a perfect defense against Mongol tribes. Chinese influence would reach as far as Central Asia. Korea became a vassal state, while Tonkin and Yue were annexed into the empire. The Vietnamese faced invasion from China, but were resistant to domination. This explains why the northern part of Vietnam has elements of Chinese culture. India and China became dominant forces, but other Asian states contributed to the development of the continent.
Japan and Korea followed a some what different path. They were influenced by Chinese culture, but still had unique indigenous cultural identity. Many peoples of Southeast Asia can trace their ancestry back to the migration of the Mon tribes of China. This part of Asia was developing significant cultural and economic ties to India. Empires and kingdoms developed from this trade and migration. The Khmer Empire arose in the 6th century C.E. and fell by the 15th century. The Khmer people invaded from South China, then took the Mekong Valley. The Funanese who were the original inhabitants were absorbed. The Khmers established a great cultural center important to Buddhist history known as Angkor. Champa was a Vietnamese kingdom that emerged by the Malay Chams. Myanmar's history as a unified state began with the Tibetan Pyu. When land contact was made, trade with India increased its power. Their Thai competitors attacked them in 835. They were raiders with limited ambition for empire building. The Burmese would then create a more stable unified state basing the capital at Pagan. The Burmese centuries later would exact vengeance with the invasion of the Thai capital Ayutthia in 1569. Korea's path was one of occupation, division, and eventual reunification. Around the 4th century B.C.E Tungusic tribes settled the lands. China then put Korea in a vassal state position. They occupied areas of northwestern Korea from 108 B.C.E to 313. The problem was that there were three rival kingdoms. As Koreans fought among themselves, this allowed China to have more leverage in the region. The Koguryo Kingdom took unilateral action by expelling the Chinese. The Korean peninsula was united by the 660s under the rule of the Silla dynasty. When that ruling family lost power the Koryo dynasty was the successor ( 936- 1392). King Yi who overthrew the Koryo moved the state closer to China in policy and adopted neo-Confucius principles.
Japan's history was between opening up to other states or complete isolation from the world. The suspicion of foreigners may seem xenophobic, but in the context of Asia's past it seemed practical. War and invasions were common, just like any other continent. Japan became even more suspicious with arrival of Europeans to Asia. When contact was made it was a signal to modernize and build its military. These was a task Japan could handle considering it was able to stop Mongol and Chinese invasions.
From the early common era to the 17th century Turkish nomads were building empires of their own. Simultaneously, Arabs were spreading Islam to the world. The Muslim caliphates would be established in Baghdad and Damascus. The Umayyad Caliphate appeared in 661. The Abbasid Caliphate would last from 762 to 1258. The Muslim conquest would expand from North Africa, Spain, and northwestern India in the Sind Valley. Arab control of Islamic civilization waned and shifted to Persia in the late 700s. Around 1055 the Seljuk Empire arose taking Baghdad as a prize. Nothing prepared them for the onslaught of Genghis Khan, who formed the largest land empire in history. Timur another Turko-Mongol warrior would establish an empire based around Persia and Iraq in the late 14th century. The Ottoman Turks were the ones to dismantle Byzantium by the invasion of Constantinople in 1453. It maintained dominance of the Middle East until its collapse in 1918. There were other lands that maintained independence such as Afghanistan, Persia, and India. Conflicts still happened between neighbors. India faced invasion from the Afghan King Mahmud of Ghazni in 1000. Muslim conquerors entered India multiple times, but were only able to establish a permanent state in 1206. This was known as the Delhi Sultanate. Muslims then had a foothold in the Indian subcontinent. The Moghuls owe their success to that early Muslim kingdom. While India and Persia faced invasion and a process of regaining independence, China adjusted differently to foreign invaders. The conquerors would become sinicized, meaning they adopted Chinese culture and governance systems. China's dynastic periods of the Tang ( 618- 906), Northern Song (906-1127), and Sung (1127- 1279) saw the rise of high cultural achievement. There artistic and scientific achievements were so impressive, that Mongol rulers adopted their ideas. Kublai Khan the Mongol ruler seemed to favor Chinese culture more than his Mongol culture. The Yuan dynasty (1271-1368) even though it had Mongol leaders was still at its heart culturally sinicized. The following dynasty was the Ming (1368-1644), which was indigenous. Then the Manchus invaded and would remain in power until 1911. The Qing dynasty did not fall from an invader, but a public that was no longer willing to tolerate their rule. When the Turko-Mongols hold on Central Asia and Siberia weakened Slavic peoples from Europe began to colonized the land.
Tartars and Turko-Mongols had to compete against Europeans that were taking their land. Russia's rise as an empire would subject Turkish and Mongol peoples to domination. European contacts often lead to conflict and subjugation of Asian societies. When the Age of Exploration approached, this signaled Asia was about to face one of its biggest challenges: modern imperialism.
Spain and Portugal were the first overseas empires to establish colonies in Asia. Portugal reached Calicut, India in 1498 and their invasions did not stop there. Ceylon and the Moluccas later fell to Portuguese. The Dutch and Spanish were to follow in conquest and the opening of new routes of trade. Spain took the Philippines, while the Dutch acquired Java. The Dutch also challenged the Portuguese holdings in the Moluccas. Besides loss of territory, European arrivals brought economic domination. The Dutch, British, and French discovered the best way to exploit Asia was through East India Companies. Asians were gradually losing control of their continent. The British East India Company became more powerful than the others due to the fact the British Navy ensured this. The British Empire was the most powerful on Earth and therefore had predominance economically. Robert Clive is credited for making the British East India Company a potent force and ensuring British control of India. Northern and Central Asia were not insulated from events. These areas faced Russian invasion. The end of the 18th century brought more European attacks to Asia. These resulted in numerous independent states losing their freedom. The British invaded Ceylon in 1815 and annexed Burma to its empire in 1886. Direct rule of India came in 1857. The British attempted to add Afghanistan to its domains, but was defeated. Singapore was subjugated in 1819 and the Malay peninsula was fully absorbed in 1874. The British then decided to put Borneo under a protectorate status in 1888. Although there were many brutal invasions, there were still some states that maintained independence. Japan and Siam were the exceptions. Japan was forced to come out of isolation when the US threatened it with war. Commodore Matthew C. Perry forced Japan to open up its market and accept a commercial treaty. The Meiji Restoration was the point in which Japan asserted its self against European intrusion in its affairs. From 1868 to 1910 Japan became a modern empire taking possession of Formosa (1895) and Korea ( formally annexed in 1910). Japan's greatest victory was the beating of Russia in the Russo-Japanese War( 1904- 1905). This was a shock to European powers, that an Asian nation could subdue a European empire militarily.Besides the British presence, the French held Cambodia (1863), Laos ( 1893) and Vietnam (1885). The French combined all these colonies and protectorates into the Indochinese Union in 1887. China was divided into spheres of influence by European powers under the Open Door policy. Japan also gained spheres of influence and territory after the Sino-Japanese War ( 1894-1895). China was not colonized directly, because of its vast size and difficult terrain, but lost control of its economic and internal affairs.
The Dutch did not have as much as the larger powers, but still maintained Indonesia. The US was a new comer to the region and took the Philippines after the Spanish-American War. Russia made a larger military advancement into Central Asia, invading Samarkand and Bhukara by 1868. Russia also added Khiva (1873) to its collection of Central Asian possessions. The British made the Suez Canal a useful trade pathway and continued to conquer more of West Asia. Aden had been a place that the British seized in 1839, which became a launching pad for other intrusions into the Middle East. Iran would face pressure from both the British and Russian Empire. Europe by the 20th century dominated most of Asia. Imperialism had a negative repercussion. When most of the world was conquered by only a few empires, it was only inevitable that they would go to war. A combination of rabid nationalism,militarism, ethnic hatred, and rival alliance systems started World War I. This war was immense in scale, involving colonial troops from all around the world. Asia was about to under go political changes.
World War I resulted in a change in the geopolitical landscape. The German, Russian, and Ottoman empires disappeared. New states would emerge. Turkey would become a republic in 1923 and the Arab lands would fall under European colonization through the mandate system. The British added Transjordan, Palestine, and Iraq to its territories. Syria and Lebanon would be dominated by the French. Iraq gained independence in name only in 1921, but in reality was still controlled indirectly by the British. Iran saw a change in regime with the rise of the Pahlavi dynasty in 1925. The newly formed Soviet Union was attempting to stop the Basmachi revolt. This was an armed movement of the Central Asian states who wanted independence. It began in 1916 a political issue inherited from the Czarist regime. The rebellion ended in 1934 with the Soviet Union fully incorporating their Central Asian colonies. The Soviet Union would also gain influence in Mongolia. Before it separated from China in 1911, but could not counter Soviet power. The reason Mongolia became important was that it provided a buffer zone against a more aggressive Japan. Japan wanted to expand its empire into what was referred to as the greater East Asia co-prosperity sphere. Japan invaded Manchuria in 1931 and declared full scale war on China in 1937. It believed it had the right to rule over all of Asia, rather than the European occupiers. Tension arose between Japan, the US, Britain, and France. When war broke out in Europe in 1939, it weakened Britain and France. Japan which forged an alliance with Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy had a free hand to take Asian colonies from the Allied powers. The Axis alliance seemed as if they were going to win World War II. Military and political miscalculations reversed the tide.
When Japan bolted through Asia during World War II this ended European domination of the continent. Indochina was taken when France fell to Germany. The Japanese threatened India and Australia. The Axis reached their pinnacle of power in 1942. Gradually the Axis lost territory and tactical advantage. Japan and Germany never fully coordinated their attacks on the Allies. Japan signed a neutrality pact with the Soviet Union in 1941. Hitler hoped that his Far east ally would wage war on the Soviet Union. This would mean that the Soviets could be cornered, force to fight on two fronts.Japan refused, but had trouble subduing China. The Chinese Communist Party and the Kuomingtang collaborated in expelling Japanese forces. It was the Chinese Civil War, which caused disunity in China. After the removal of the warlords the Kuomingtang and the Communist fought for control. The Japanese Empire used this internal disorder to slowly conquer China. The war in Europe ended before the war in the Pacific. Japan continued to fight on until it was attacked with nuclear weapons. Hiroshima and Nagasaki were devastated and Japan surrendered ending World War II. The decision that US made of using the atom bomb remains controversial to this day. Europe was in ruins and it was impossible for them to reassert the colonial order. Asians had seen that the West was not invincible and fought for freedom.
Decolonization after World War II swept around the Asian continent. India was granted independence from the British Empire in 1947. Burma and Ceylon freed themselves of the British yoke in 1948. The Dutch were driven from Indonesia in 1949. The mandate system was dissolving and new states were formed in the Middle East. The rapid decolonization process did have political complications. The colonizers that made boundaries without consideration to ethnic,religious, and regional tensions. The point of doing this was to divide and rule, so that the masses would not revolt .India would find itself in conflict with Pakistan throughout most of the 20th century stemming from Muslim and Hindu conflict. There were divisions among Arabs, Turks, and Kurds. This was complicated further with the establishment of Israel in 1948. The influx of Jewish refugees from Eastern Europe came displacing Palestinians. Decolonization became intertwined with Cold War politics.Korea and Vietnam faced challenging struggles to obtain national sovereignty. The Vietnamese defeated the French in 1954, but the country was still divided between a Communist north and a West leaning south. The Vietminh had fought the Japanese in World War II, the French, and would later face the United States. The Vietminh was focused more on Vietnamese nationalism rather than seeking political alliance with China or Russia.China and Vietnam had animosity for each other dating back as far as the Tang dynasty. Vietnam was able to play both Russia and China off against each other to get aid. The US during the early years of the Cold War saw communism as monolithic; they were merely puppets of the Soviet Union. This was not true, due to the fact that under Nikita Khrushchev relations with China deteriorated. Mao Zedong did not like Khrushchev's reforms in Russia.Maoism was different in theory and practice than Russian communism. The US did not only target Russia in its anti-communist crusade, China, Indonesia, and Vietnam were marks for harassment. This was the containment policy. The US was going to attempt to stop the spread of communism by intervening directly or covertly around the globe. The US went to Vietnam in an advisory role supporting the South Vietnamese government against North Vietnam. Around 1965 direct intervention occurred later engulfing Laos and Cambodia. Sukarno was deposed in Indonesia by a CIA plot with the military due to his anti-colonial stance and his acceptance of the PKI. The PKI was the largest communist party outside both Russia and China. The Korean War ended in 1953 with a cease-fire and ever since their has been hostility between North Korea and the US. The intervention that happened in Korea was something the US did not want to repeat in Vietnam. Being an occupying force lead to America's defeat and Vietnam would unify under communist rule in 1975. The 20th century witnessed a series of Indo-Pakistani Wars, Arab-Israeli Wars, and the Sino-Vietnamese War of 1979. Myanmar, Indonesia, Malaysia, and the Philippines saw the development of internal rebellions and insurgencies. The Asian continent has still been recovering from conflicts of the Cold War.
The 21st century demonstrates that global economic power is shifting. China has risen both economically and militarily. Other Asian nations became economically mobile like Taiwan, Singapore, South Korea, and Hong Kong. These became known as the Asian tiger economies. These countries charted their own paths to development rather than suggestions by the IMF or World Bank. Japan had risen economically through the development of a remarkable electronics and automobile industry. While other nations rose, others continue to struggle. Laos, Cambodia, Indonesia, Malaysia , Vietnam,, and Myanmar struggle with poverty and a low standard of living. China has developed a strong economy, but the rural poor have seen no benefits. The market reforms that were implemented by Deng Xiaoping had devastating consequences. Rural poor now migrate to the cities for work. There they labor in unreasonable conditions for minimal pay. Income disparity continues to grow been the privileged elite and the working majority. West Asia also saw a shift. As more people became dissatisfied with their leaders, the movement to radical political Islamism became stronger. US interventions and involvement in Iraq and Afghanistan caused mass destabilization. Saddam Hussein once a US ally, became an enemy after Iraq invaded Kuwait in 1990. After Iraq's removal from Kuwait the US continued to have military bases in Saudi Arabia and other Gulf monarchy states . Combined with the continued support of Israel and support for regimes that Arabs reject, the image of the US became unfavorable in regional public opinion. A more powerful China in the East has caused tension among Vietnam, Japan, the Philippines, and Indonesia. The South China Sea dispute has divided Asia. The US has taken note of this, by attempting to make Asia Pacific a sphere influence once more. India has been increasing its regional power for the past decade. There are even rumors it seeks to make sustainable peace with Pakistan. There has been a long history of conflict between Asian nations, but at this time it could mean the loss of independence from external forces. It is impossible to predict the future, but it appears as if Asia is on the rise once more.
Further Reading
"Asia." Encyclopedia of Knowledge. Vol. 2. Danbury, CT: Grolier, 1991. 201-08.











No comments:
Post a Comment